
As the healthcare industry increasingly relies on digital solutions to store and manage sensitive patient data, the need for robust cybersecurity has never been more pressing. With cybercriminals targeting healthcare organizations, data breaches have become a major concern. Healthcare data—including personal health information (PHI), medical histories, social security numbers, and financial records—are high-value targets for attackers. Any breach could not only cause significant damage to the organization but also compromise the privacy and safety of millions of patients.
In fact, last month, University of Washington Medicine revealed that nearly one million patient records had been exposed online, underscoring the importance of protecting healthcare data. Healthcare providers, health plans, and other regulated organizations must adhere to strict data protection protocols to safeguard patient information. The failure to do so can result in hefty fines, loss of patient trust, and damage to a healthcare organization’s reputation.
What Are Healthcare Data Breaches?
Healthcare data breaches refer to incidents where sensitive information is accessed or disclosed without authorization. This could occur due to:
- Theft of physical or digital records
- Unauthorized access to accounts or systems
- Malicious hacking incidents
While paper records were once the primary source of data breaches, network servers and emails are now the most commonly breached media in healthcare. Criminal hackers increasingly use phishing techniques to gain unauthorized access to electronic records, highlighting the need for stronger protection against cyber threats.
Are Healthcare Data Breaches on the Rise?
According to the latest HIPAA figures, healthcare data breaches have increased dramatically in recent years. In just the past year, a staggering 15 million patient records were exposed, with the number of breaches rising each quarter. Hacking and IT incidents account for nearly half of all data breaches, with insider threats also remaining a significant concern.
The rise in cyberattacks on healthcare organizations is compounded by the fact that Personal Health Records (PHR) are highly sought after on the black market. These records can be used for identity theft, fraudulent purchases, and even opening fake accounts, making healthcare a prime target for cybercriminals.
What Are the Impacts of Healthcare Data Breaches?
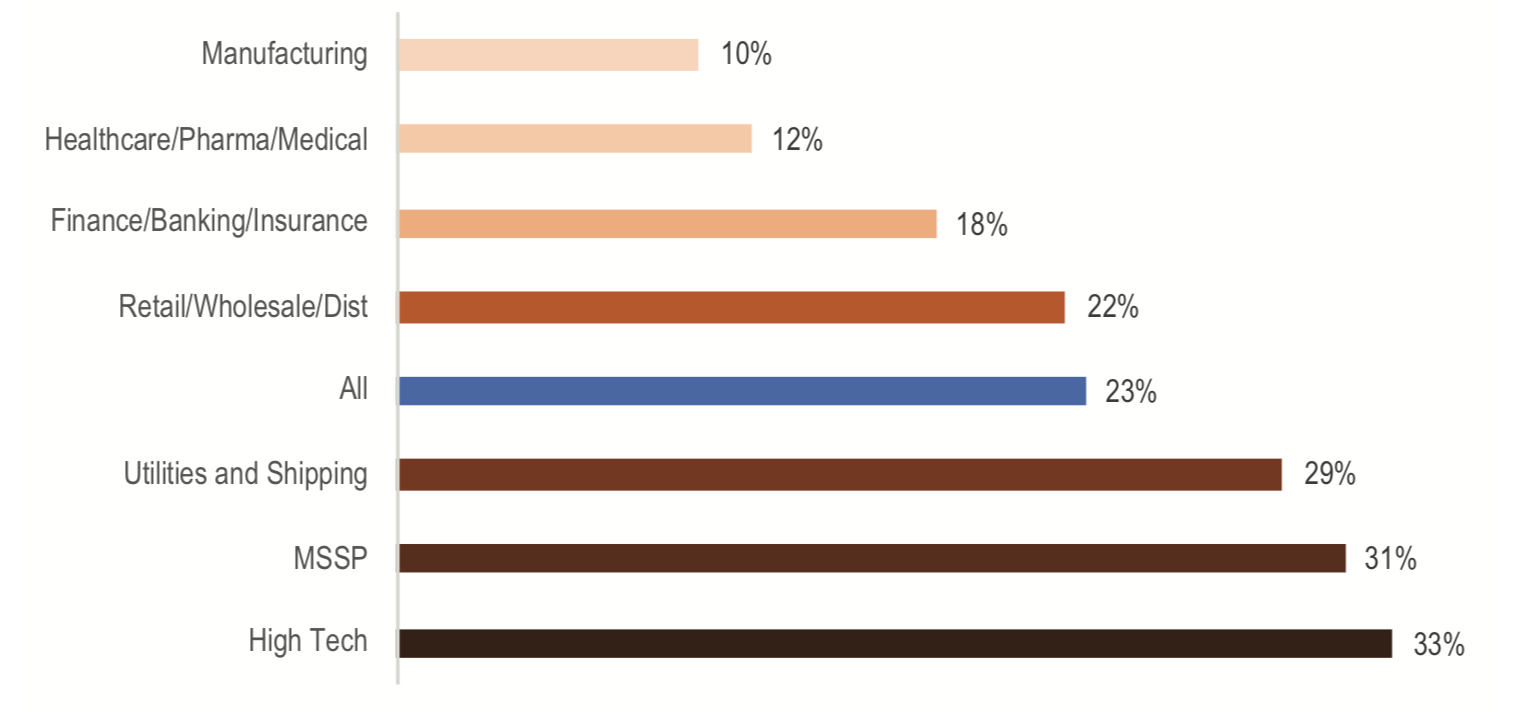
The financial impact of a data breach in healthcare is substantial. The Ponemon Institute reports that the cost per record exposed in healthcare breaches is significantly higher than in other industries, such as finance. For example, the cost of a breach due to hacking is often double that of other causes, underscoring the need for advanced cybersecurity solutions to mitigate the risks.
In addition to financial losses, healthcare organizations may face regulatory fines and loss of consumer trust. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has the authority to impose penalties on organizations that violate HIPAA guidelines, adding another layer of pressure on healthcare providers to protect patient data.
7 Best Practices for Healthcare Security
Here are seven best practices to help healthcare organizations safeguard their data and reduce the risk of cyberattacks:
1. Use Next-Generation Security Software
Traditional antivirus software has multiple blind spots and can’t provide the deep visibility required to defend against modern threats. Next-generation antivirus (NGAV) solutions, powered by AI and machine learning, offer a more proactive approach to detecting and blocking malware, phishing attempts, and ransomware. Healthcare organizations should invest in NGAV software that can detect intrusions, block malicious activity, and provide comprehensive visibility into endpoint behavior.
2. Lock Down Your Endpoints
Endpoints—such as computers, mobile devices, and medical equipment—are common entry points for cyberattacks. Healthcare providers must implement strict controls to prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to their networks. Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP) should be used to control physical access to machines and monitor all devices connected to the network to detect potential threats before they can cause harm.
3. Restrict and Monitor Network Traffic
To prevent malware from entering your network, it’s critical to manage network traffic. Healthcare providers should implement policies that govern permitted communications between devices and prevent connections to known malicious sites. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) can help ensure that only authorized network traffic flows, reducing the likelihood of a breach.
4. Automate Software Updates
Unpatched software is one of the most common vulnerabilities that hackers exploit to gain access to healthcare systems. Organizations should automate the process of patching operating systems and third-party software. This ensures that all vulnerabilities are addressed quickly and reduces the attack surface by keeping systems up to date with the latest security patches.
5. Don’t Rely on Reputation
It’s not enough to simply trust software based on its reputation. Hackers can hijack trusted update servers or exploit vulnerabilities in trusted vendors. Healthcare organizations should use security solutions that analyze the behavior of processes, rather than relying on the identity of the software. This approach helps to detect malicious activity, even if the source appears legitimate.
6. Watch Out for IoT Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly prevalent in healthcare, but these connected devices can present significant security risks if not properly secured. IoT devices, including medical equipment and wearables, should be closely monitored for vulnerabilities. Security solutions like SentinelOne Ranger can help organizations keep track of all devices connected to the network, ensuring that unmanaged endpoints are identified and secured.
7. Have an Incident Response Plan
Healthcare organizations must be prepared for the inevitable security incident. An incident response plan should outline the steps to take in the event of a breach. This plan should be regularly tested and updated to ensure it is effective and that staff are familiar with the procedures. The quicker an organization can identify and respond to a breach, the less damage it will cause.
Read More: SentinelOne: A Leader in the 2025 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Endpoint Protection
Conclusion: Protecting Healthcare Data in a Complex Threat Landscape
Healthcare data breaches are on the rise, and the consequences can be devastating for both organizations and patients. To protect sensitive data and comply with regulations like HIPAA, healthcare providers must adopt a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By following these seven best practices—investing in next-gen security software, securing endpoints, automating updates, and more—healthcare organizations can reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats.
SentinelOne, with its advanced endpoint protection and AI-driven solutions, provides healthcare organizations with the tools they need to detect, respond to, and prevent cyberattacks. By taking proactive measures and adopting the right technology, healthcare providers can protect patient data, minimize the financial impact of data breaches, and maintain the trust of their patients.
Refrence :
https://www.sentinelone.com/blog/healthcare-data-under-attack-7-best-practices



